Remote or Unguided Media or Unbound Transmission Media:
Unbound transmission media are the methods for transmitting information without utilizing any links. These media are not limited by physical geography. This kind of transmission is called Wireless communication. These days remote(wireless) communication is become populer. Remote LANs are being introduced in office and school grounds. This transmission utilizes Microwave, Radio wave, Infra red are some of prominent unbound transmission media.
The data transmission capabilities of various Medias vary differently depending upon the various factors. These factors are:
1. Bandwidth.
It refers to the data transferring capacity of a channel or link. maximum bandwidth communication links support maximum data rates.
2. Radiation.
It refers to the outflow of signal from the channel due to unwanted electrical appearance of the channel.
3. Noise Absorption.
It refers to the susceptibility of the media to external electrical noise that can cause distortion of data signal.
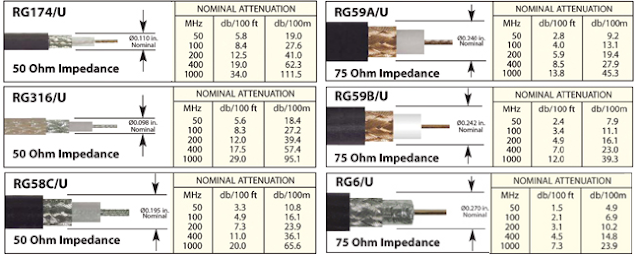
4. Attenuation.
It refers to loss of energy as signal propagates outwards. The amount of energy lost depends on frequency. Radiations and physical characteristics of media contribute to attenuation.